The Advancements Of Civil Engineering In Smart Grid Infrastructure For Energy Management

The Smart Grid Infrastructure in India is expected to witness high growth in the coming years. With the increasing use of renewable energy sources, the Indian government is heavily investing in upgrading the country's power infrastructure. The Smart Grid Infrastructure is a modernized electrical grid system that uses digital communications technology to detect and react to changes in the electrical supply and demand.
The Indian government is keen to adopt Smart Grid Infrastructure to increase energy efficiency, reliability, and security. It will help to reduce the country's reliance on fossil fuels and promote the use of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
The Smart Grid Infrastructure is expected to bring about significant changes in the way power is generated, transmitted, and distributed in the country. It will enable effective demand response management, reduce power outages, and improve the quality of power supply. In the long run, it will help to reduce energy costs and carbon emissions.
This article provides an in-depth look at the Indian Smart Grid Infrastructure and answers some frequently asked questions on the topic.
What is Smart Grid Infrastructure?
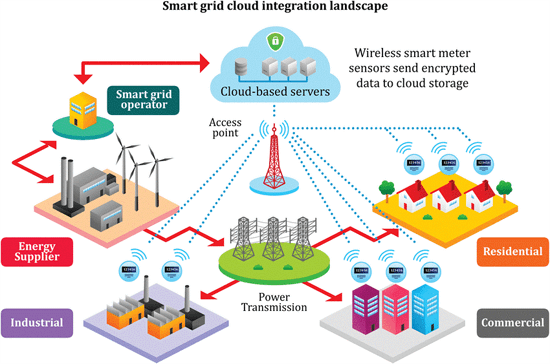
The Smart Grid Infrastructure is a modernized electrical grid system that uses digital communications technology to detect and react to changes in the electrical supply and demand. It consists of advanced sensors, communication systems, and software that enable bi-directional flow and real-time control of electricity generation, transmission, and distribution.
The Smart Grid Infrastructure helps to optimize energy management, reduce energy losses, and improve the reliability and security of the power supply. It is also instrumental in promoting the use of renewable energy sources and reducing carbon emissions.
Why is India Investing in Smart Grid Infrastructure?
The Indian government is heavily investing in upgrading the country's power infrastructure to meet the growing demand for electricity. The Smart Grid Infrastructure plays a crucial role in achieving this goal by enabling efficient energy management, improving the grid's reliability, and promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
India has set an ambitious target to achieve 175GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022. The Smart Grid Infrastructure will help to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid system seamlessly and effectively.
The Smart Grid Infrastructure will also help to reduce the country's dependence on fossil fuels. India imports more than 80% of its oil and gas needs, making it vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. By promoting the use of renewable energy sources and adopting Smart Grid Infrastructure, India can reduce its dependence on foreign oil and increase its energy security.
What are the benefits of Smart Grid Infrastructure in India?
The Smart Grid Infrastructure has several benefits for the Indian power sector, including:
- Improved Energy Efficiency: The Smart Grid Infrastructure enables efficient energy management by reducing energy losses in transmission and distribution. It also enables demand response management by providing real-time information on power usage and pricing.
- Better Grid Reliability: The Smart Grid Infrastructure helps to reduce the frequency and duration of power outages by enabling real-time monitoring and control of the power supply.
- Promoting Renewable Energy Sources: The Smart Grid Infrastructure facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the grid system seamlessly.
- Reducing Carbon Emissions: The Smart Grid Infrastructure promotes the use of renewable energy sources, which significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to global efforts to address climate change.
What are the challenges of implementing Smart Grid Infrastructure in India?
The implementation of Smart Grid Infrastructure in India faces several challenges, including:
- Technological challenges: The implementation of Smart Grid Infrastructure requires advanced technology, which may not be readily available in India. The country may need to import technology and software solutions from other countries.
- Funding challenges: The implementation of Smart Grid Infrastructure requires significant capital investment, which may not be readily available in India. The government may need to seek funding from international organizations and institutions.
- Infrastructure challenges: The implementation of Smart Grid Infrastructure requires the upgrading of the existing power infrastructure, which may be time-consuming and costly.
Conclusion
The Smart Grid Infrastructure is an essential component of the modernized electrical grid system that the Indian government is investing in. It enables efficient energy management, improves grid reliability, and promotes the use of renewable energy sources. The implementation of Smart Grid Infrastructure in India faces several challenges, but the benefits it provides make it a worthwhile investment for the country's future energy needs.
With the growing demand for electricity and the need to reduce carbon emissions, India's investment in Smart Grid Infrastructure is a step in the right direction towards achieving a sustainable energy future.

Post a Comment for "The Advancements Of Civil Engineering In Smart Grid Infrastructure For Energy Management"